 Christin Hume – Unsplash
Christin Hume – UnsplashFrance Bans Forever Chemicals in Cosmetics, Fashion, and Ski Wax
 Christin Hume – Unsplash
Christin Hume – UnsplashThe world’s carbon emissions continue to rise. But 35 countries show progress in cutting carbon
Global fossil fuel emissions are projected to rise in 2025 to a new all-time high, with all sources – coal, gas, and oil – contributing to the increase.
At the same time, our new global snapshot of carbon dioxide emissions and carbon sinks shows at least 35 countries have a plan to decarbonise. Australia, Germany, New Zealand and many others have shown statistically significant declines in fossil carbon emissions during the past decade, while their economies have continued to grow. China’s emissions have also been been growing at a much slower pace than recent trends and might even be flat by year’s end.
As world leaders and delegates meet in Brazil for the United Nations’ global climate summit, COP30, many countries that have submitted new emissions commitments to 2035 have shown increased ambition.
But unless these efforts are scaled up substantially, current global temperature trends are projected to significantly exceed the Paris Agreement target that aims to keep warming well below 2°C.
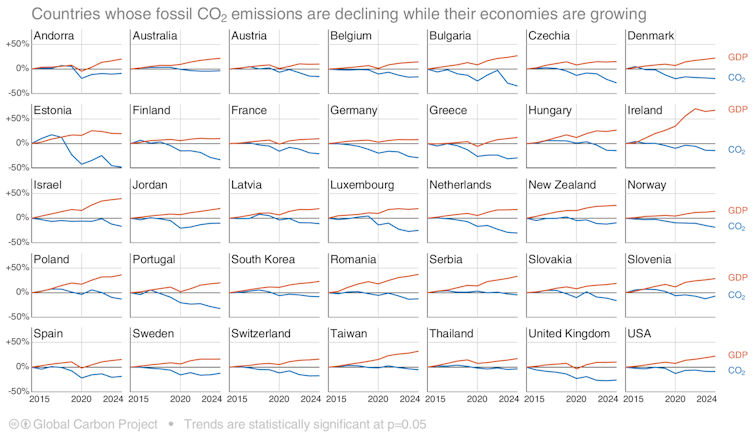 These 35 countries are now emitting less carbon dioxide even as their economies grow. Global Carbon Project 2025, CC BY-NC-ND
These 35 countries are now emitting less carbon dioxide even as their economies grow. Global Carbon Project 2025, CC BY-NC-NDFossil fuel emissions up again in 2025
Together with colleagues from 102 research institutions worldwide, the Global Carbon Project today releases the Global Carbon Budget 2025. This is an annual stocktake of the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide worldwide.
We also publish the major scientific advances enabling us to pinpoint the global human and natural sources and sinks of carbon dioxide with higher confidence. Carbon sinks are natural or artificial systems such as forests which absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than they release.
Global CO₂ emissions from the use of fossil fuels continue to increase. They are set to rise by 1.1% in 2025, on top of a similar rise in 2024. All fossil fuels are contributing to the rise. Emissions from natural gas grew 1.3%, followed by oil (up 1.0%) and coal (up 0.8%). Altogether, fossil fuels produced 38.1 billion tonnes of CO₂ in 2025.
Not all the news is bad. Our research finds emissions from the top emitter, China (32% of global CO₂ emissions) will increase significantly more slowly below its growth over the past decade, with a modest 0.4% increase. Emissions from India (8% of global) are projected to increase by 1.4%, also below recent trends.
However, emissions from the United States (13% of global) and the European Union (6% of global) are expected to grow above recent trends. For the US, a projected growth of 1.9% is driven by a colder start to the year, increased liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports, increased coal use, and higher demand for electricity.
EU emissions are expected to grow 0.4%, linked to lower hydropower and wind output due to weather. This led to increased electricity generation from LNG. Uncertainties in currently available data also include the possibility of no growth or a small decline.
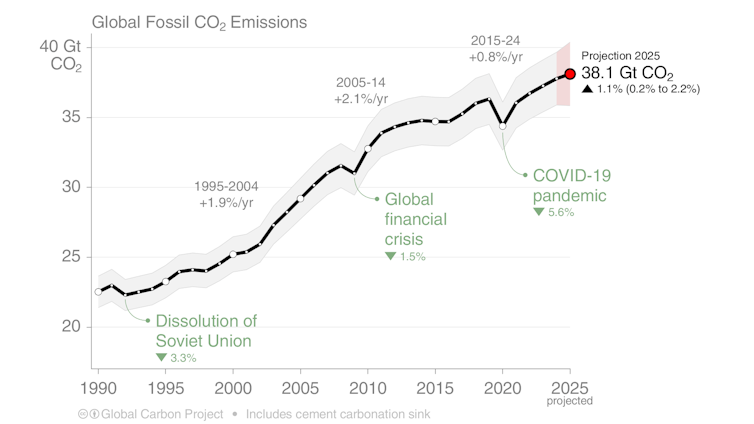 Fossil fuel emissions hit a new high in 2025, but the growth rate is slowing and there are encouraging signs from countries cutting emissions. Global Carbon Project 2025, CC BY-NC-ND
Fossil fuel emissions hit a new high in 2025, but the growth rate is slowing and there are encouraging signs from countries cutting emissions. Global Carbon Project 2025, CC BY-NC-NDDrop in land use emissions
In positive news, net carbon emissions from changes to land use such as deforestation, degradation and reforestation have declined over the past decade. They are expected to produce 4.1 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide in 2025 down from the annual average of 5 billion tonnes over the past decade. Permanent deforestation remains the largest source of emissions. This figure also takes into account the 2.2 billion tonnes of carbon soaked up by human-driven reforestation annually.
Three countries – Brazil, Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo – contribute 57% of global net land-use change CO₂ emissions.
When we combine the net emissions from land-use change and fossil fuels, we find total global human-caused emissions will reach 42.2 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide in 2025. This total has grown 0.3% annually over the past decade, compared with 1.9% in the previous one (2005–14).
Carbon sinks largely stagnant
Natural carbon sinks in the ocean and terrestrial ecosystems remove about half of all human-caused carbon emissions. But our new data suggests these sinks are not growing as we would expect.
The ocean carbon sink has been relatively stagnant since 2016, largely because of climate variability and impacts from ocean heatwaves.
The land CO₂ sink has been relatively stagnant since 2000, with a significant decline in 2024 due to warmer El Niño conditions on top of record global warming. Preliminary estimates for 2025 show a recovery of this sink to pre-El Niño levels.
Since 1960, the negative effects of climate change on the natural carbon sinks, particularly on the land sink, have suppressed a fraction of the full sink potential. This has left more CO₂ in the atmosphere, with an increase in the CO₂ concentration by an additional 8 parts per million. This year, atmospheric CO₂ levels are expected to reach just above 425 ppm.
Tracking global progress
Despite the continued global rise of carbon emissions, there are clear signs of progress towards lower-carbon energy and land use in our data.
There are now 35 countries that have reduced their fossil carbon emissions over the past decade, while still growing their economy. Many more, including China, are shifting to cleaner energy production. This has led to a significant slowdown of emissions growth.
Existing policies supporting national emissions cuts under the Paris Agreement are projected to lead to global warming of 2.8°C above preindustrial levels by the end of this century.
This is an improvement over the previous assessment of 3.1°C, although methodological changes also contributed to the lower warming projection. New emissions cut commitments to 2035, for those countries that have submitted them, show increased mitigation ambition.
This level of expected mitigation falls still far short of what is needed to meet the Paris Agreement goal of keeping warming well below 2°C.
At current levels of emissions, we calculate that the remaining global carbon budget – the carbon dioxide still able to be emitted before reaching specific global temperatures (averaged over multiple years) – will be used up in four years for 1.5°C (170 gigatonnes remaining), 12 years for 1.7°C (525 Gt) and 25 years for 2°C (1,055 Gt).
Falling short
Our improved and updated global carbon budget shows the relentless global increase of fossil fuel CO₂ emissions. But it also shows detectable and measurable progress towards decarbonisation in many countries.
The recovery of the natural CO₂ sinks is a positive finding. But large year-to-year variability shows the high sensitivity of these sinks to heat and drought.
Overall, this year’s carbon report card shows we have fallen short, again, of reaching a global peak in fossil fuel use. We are yet to begin the rapid decline in carbon emissions needed to stabilise the climate.![]()
Pep Canadell, Chief Research Scientist, CSIRO Environment; Executive Director, Global Carbon Project, CSIRO; Clemens Schwingshackl, Senior Researcher in Climate Science, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich; Corinne Le Quéré, Royal Society Research Professor of Climate Change Science, University of East Anglia; Glen Peters, Senior Researcher, Center for International Climate and Environment Research - Oslo; Judith Hauck, Helmholtz Young Investigator group leader and deputy head, Marine Biogeosciences section at the Alfred Wegener Institute, Universität Bremen; Julia Pongratz, Professor of Physical Geography and Land Use Systems, Department of Geography, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich; Mike O'Sullivan, Lecturer in Mathematics and Statistics, University of Exeter; Pierre Friedlingstein, Chair, Mathematical Modelling of Climate, University of Exeter, and Robbie Andrew, Senior Researcher, Center for International Climate and Environment Research - Oslo
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Over 2,000 flights cancelled across US as federal govt shutdown enters day 40
 Representational photo. (IANS Photo)
Representational photo. (IANS Photo)